Readmore »»
Diposkan oleh Welly Agung Kusuma Riva, S.Kom. NUPTK:2563756658200023 di 00:53 0 komentar
Label: NOS
Diposkan oleh Welly Agung Kusuma Riva, S.Kom. NUPTK:2563756658200023 di 02:19 0 komentar
Label: Keamanan Jarkom

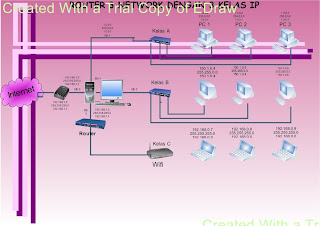
Network Operating System Features

| Lapisan ke- | Nama lapisan | Keterangan |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | Application layer | Berfungsi sebagai antarmuka dengan aplikasi dengan fungsionalitas jaringan, mengatur bagaimana aplikasi dapat mengakses jaringan, dan kemudian membuat pesan-pesan kesalahan. Protokol yang berada dalam lapisan ini adalah HTTP, FTP, SMTP, dan NFS. |
| 6 | Presentation layer | Berfungsi untuk mentranslasikan data yang hendak ditransmisikan oleh aplikasi ke dalam format yang dapat ditransmisikan melalui jaringan. Protokol yang berada dalam level ini adalah perangkat lunak redirektor (redirector software), seperti layanan Workstation (dalam Windows NT) dan jugaNetwork shell (semacam Virtual Network Computing (VNC) atau Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)). |
| 5 | Session layer | Berfungsi untuk mendefinisikan bagaimana koneksi dapat dibuat, dipelihara, atau dihancurkan. Selain itu, di level ini juga dilakukan resolusi nama. |
| 4 | Transport layer | Berfungsi untuk memecah data ke dalam paket-paket data serta memberikan nomor urut ke paket-paket tersebut sehingga dapat disusun kembali pada sisi tujuan setelah diterima. Selain itu, pada level ini juga membuat sebuah tanda bahwa paket diterima dengan sukses (acknowledgement), dan mentransmisikan ulang terhadp paket-paket yang hilang di tengah jalan. |
| 3 | Network layer | Berfungsi untuk mendefinisikan alamat-alamat IP, membuat header untukpaket-paket, dan kemudian melakukan routing melalui internetworking dengan menggunakan router dan switch layer-3. |
| 2 | Data-link layer | Befungsi untuk menentukan bagaimana bit-bit data dikelompokkan menjadi format yang disebut sebagai frame. Selain itu, pada level ini terjadi koreksi kesalahan, flow control, pengalamatan perangkat keras (seperti halnya Media Access Control Address (MAC Address)), dan menetukan bagaimana perangkat-perangkat jaringan seperti hub, bridge, repeater, dan switch layer 2beroperasi. Spesifikasi IEEE 802, membagi level ini menjadi dua level anak, yaitu lapisan Logical Link Control (LLC) dan lapisan Media Access Control(MAC). |
| 1 | Physical layer | Berfungsi untuk mendefinisikan media transmisi jaringan, metode pensinyalan, sinkronisasi bit, arsitektur jaringan (seperti halnya Ethernet atauToken Ring), topologi jaringan dan pengabelan. Selain itu, level ini juga mendefinisikan bagaimana Network Interface Card (NIC) dapat berinteraksi dengan media kabel atau radio. |